Glossary
All Routes Lead To Rome
PILGRIMAGE TOURISM
Is the type of tourism that motivates tourists for religious attitude and practices.
TREKKING
Is a trip on the trails of relatively unspoiled natural areas with the purpose of exploring and enjoying nature.
LEGAL SETUP OF A CULTURAL ROUTE
Can have the form of an Association or Foundation or other similar types operating on a non-profit basis, or could be a company.
POINTS OF INTEREST OF A CULTURAL ROUTE
Could include cultural or environmental heritage, local typical products, cultural events.
CULTURAL ROUTE
Is used in a more conceptual and general sense, expressing a network of sites or geographical areas sharing a theme.
Graph (or plot)
A graphical representation of data. The type of graphical representation depends on the type of variable represented. Counts and percentages are usually represented with either bar graphs or pie charts, whereas counts of data-into-classes are represented by histograms. Scores are instead represented by points and connected points, while groups are rather represented by some graph aesthetic (e.g. color, shape, point dimension).
Table
Traditional format of a collection of data. Rows usually indicate observations (e.g. individuals, customers, countries, etc.), while columns usually indicate variables (e.g. the phenomenon of interest, such as interests, market habits, features, etc). Sometimes, data is not perfectly organized and ready to be processed: let’s think, for example, of a data table retrieved from an official source, where columns display each a different year, while rows represent countries. In order to facilitate the graphical data representation, data must be transformed in order for columns to represent one single variable (in this case, all the columns belonging each to a different year should be pivoted into one column called Year, containing them all as rows): this might require data transformation operations (pivoting the table into long or wide format).
NUTS
The Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics (NUTS) is a hierarchical system dividing up the economic territory of the EU and the UK for the purpose of: • Collection, development and harmonization of European regional statistics • Socio-economic analyses of the regions. The Territorial units are divided into: o NUTS 1: major socio-economic regions o NUTS 2: basic regions for the application of regional policies o NUTS 3: small regions for specific diagnoses
Database
A database is an organized collection of data, generally stored and accessed electronically from a computer system. Databases belonging to Official Sources are available online to consult and download.
Official Sources
Official sources are reliable, credible resources based on a number of factors. It is a body of work created by an authoritative body in its field, which is widely recognized and considered as expert.
KPI (Key performance Indicators)
A Key Performance Indicator is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives.
LEAN STARTUP
The Lean Startup methodology has as a premise that every startup is a grand experiment that attempts to answer a question. Using the Lean Startup approach, companies can create order not chaos by providing tools to test a vision continuously. It is about putting a process, a methodology around the development of a product.
BUSINESS VISION
In Economics, Vision is a vivid mental image of what you want your business to be at some point in the future, realistically based on your goals and aspirations as well as on your resources, capabilities, growth potential and affordable opportunities. Having a vision is what gives your startup a clear focus, maintaining you in the right direction. It needs to be formalised and written in a vision statement that will be part of your elevator pitch and inspire your high concept pitch.
PITCH
Pitch is a word with very different meanings in different linguistic contexts. In Business, it is referred to a speech or act that attempts to persuade someone of the validity of an idea or a quality of a product in order to make her or him inclined to invest in a business, collaborate with the firm, or buy a product or a service. It has to make clear what your business is about, which is your vision and your business aim. If the goal is to raise startup cash, a pitch can be used to present the business idea to potential investors. Beside this, other pitches can be addressed to potential customers, to convince them to buy products and services. Finally, a pitch can be useful when you need a partnership with other business or new coworkers in yours.
BRAINSTORMING
It is an activity or business method in which a group of people meet to suggest a lot of new ideas for possible development or problem’s solution. People, gathered together, generate new ideas and solutions around a specific domain of interest by removing inhibitions, often with the help of one or two facilitators. In this way, people are able to think more freely and they suggest as many spontaneous new ideas as possible. All the ideas are noted down without criticism and after the brainstorming session the ideas are evaluated. The term was popularized by Alex Faickney Osborn during the Sixties.
Focus Strategy
The business canalises its effort towards a very selected market with high profitability potential.
Differential Strategy
The final output stands out not because of its cheaper price but thanks to its intrinsic characteristics. Such strategy is perfectly consistent with product/services at high innovative content, which required intense R&D efforts.
Cost leadership strategy
When firms are able to conduct the production processes at lower costs than the others, without compromising the quality of the final output.
Animal Spirits
Are humoral feelings that motivate entrepreneurial initiatives.
Entrepreneurship
Consists in creating and running a new business with the aim to generate an economic return (profit).
BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS
Is a strategic management tool and lean start up template for developing new or documenting existing business models.
CULTURAL ORGANIZATION
A cultural institution or cultural organization is an organization within a culture/subculture that works for the preservation or promotion of culture.
ENTREPRENEUSHIP EDUCATION
Is about lifelong learning and lifelong development of competencies.
ENTREPRENEUR
Individuals that transform and idea into a new business, using the overall experience, skills and initiative necessary to reach their goals.
ENTREPRENEUSHIP
Refers to the process of creating, developing and managing a new enterprise in order to gain profit by taking any of its risks in the corporate world.
The World Heritage Convention
The Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO in 1972, sets out the duties of States Parties in identifying potential sites and their role in protecting and preserving them. By signing the Convention, each country pledges to conserve not only the World Heritage sites situated on its territory, but also to protect its national heritage.
World Heritage Centre (UNESCO)
Is responsible for the day-to-day management of the Convention and for the administration of the World Heritage Fund.
European Agenda for Culture
The European Agenda for Culture and its accompanying Staff Working Document provide the framework for cooperation on culture at the EU level. These focus on the positive contribution that culture brings to Europe’s society, its economy and international relations.
Creative Europe Programme
Creative Europe is the European Commission's framework programme for support to the culture and audiovisual sectors.
European Cultural Heritage
Europe’s cultural heritage is a rich and diverse mosaic of cultural and creative expressions, an inheritance from previous generations of Europeans and a legacy for those to come.
CONTRIBUTION TO GDP
Share of the Gross Domestic Product (the total economic value generated in an economy in a given year) that can be attributed to some specific sector or activity.
3E TOURISM FORMULA
Tourism based on the presence of Excitement, Entertainment and Education in the destination to visit. Normally connected to cultural tourism.
3S TOURISM FORMULA
Tourism based on the presence of Sand, Sun and Sea in the destination to visit.
INTANGIBLE CULTURAL HERITAGE
Traditions and living expressions inherited from ancestors. Examples are oral traditions, performing arts, or crafts and rituals.
TANGIBLE CULTURAL HERITAGE
Physical artefacts that are produced, maintained and transmitted from generation to generation in society as products of human creativity that have cultural significance and can be represented by monuments, archaeological sites and objects; archive, library and audio-visual materials; objects of art, etc.
Cultural natural heritage
Countryside, natural environment, flora and fauna, bio and geo diversity, cultural landscape which is an important part of tourist industry.
Intangible and digital culture heritage
Language and knowledge, folklore, oral history, traditions customs, aesthetic and spiritual beliefs etc) which are more difficult to preserve in comparison with physical cultural goods.
Tangible culture property
Building, books, monuments, works of art, artefacts, landscapes).
Social Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur who creates businesses to address a social problem, for example, the privatization of fresh water, structural economic inequality and gentrification.
Cultural Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur who creates a business that is grounded in the arts, creatively inclined and/or is relevant to the cultural heritage of a specific community.
Feudalism
Feudalism was a combination of legal, economic, military and cultural customs that flourished in Medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or Medieval Period lasted from the 5th to the 15th century. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and merged into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery.
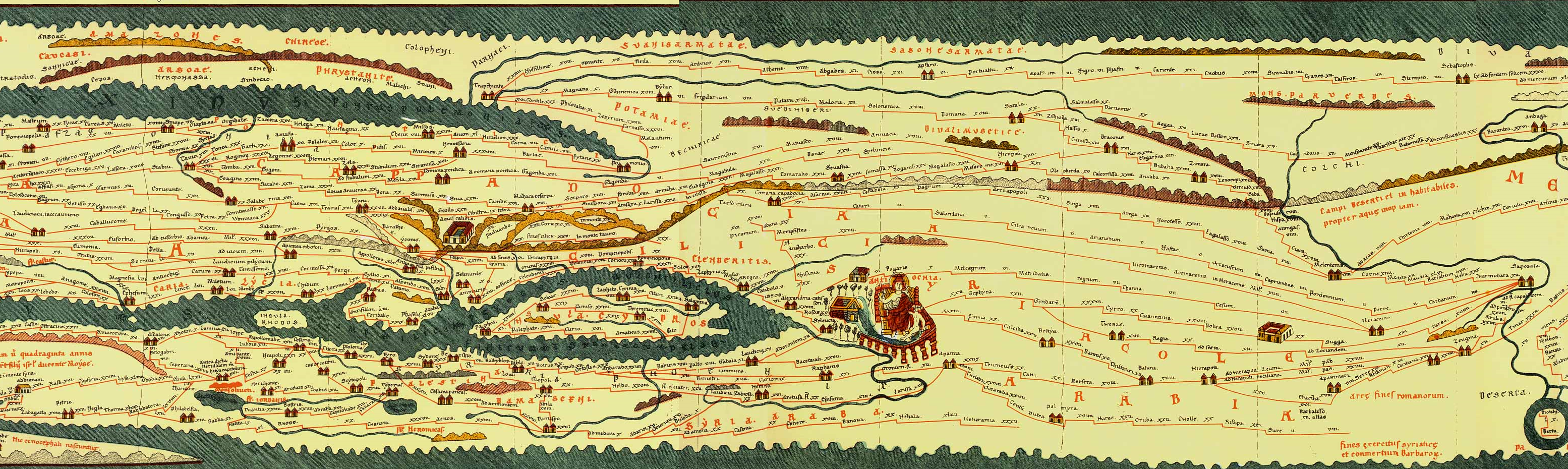
Byzantine road
The Byzantine road system is the natural continuation of the Roman one.
Stone-paved road
Road with a hard, flat surface of pieces of stone (paved with stones).
Roman legions
A Roman legion was the largest military unit of the Roman army.
BRANDING
Refers to the process of creating and developing a useful and solid brand.
SEARCH ENGINES
Informatic systems that search for files stored on web servers basing on keywords, thanks to the “web crawler”.
SEM
“Search Engine Marketing” acronym. They are paying campaigns on search engines, that allow to change online positioning. Also known as PPC or “Pay Per Click”.
SEO
“Search Engine Optimization” acronym. Is a digital marketing technique that allows to improve our page visibility to increase the traffic volume. Also known as organic or natural positioning.
RESPONSIVE DESIGN
Web design that allows to adapt the visualization to the device where we access from (tablet, smartphone, computer…)